Investing in Angola presents a myriad of opportunities and compelling reasons for investors to
consider. Here are some key factors that make Angola an attractive investment destination:
 Development Potential:
Development Potential:
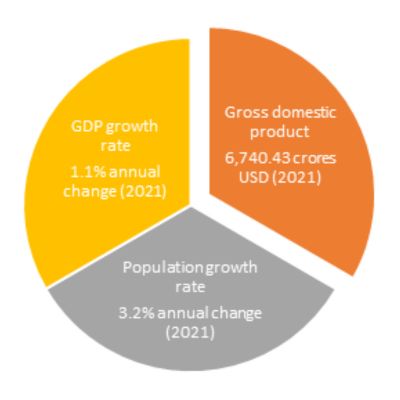
Angola possesses immense potential to emerge as one of Africa's largest and most vibrant economies. With a relatively recent history of independence and a period of prolonged civil war, the country has undergone significant economic and social modernization since 2004. Although setbacks like the drop in oil prices and the COVID-19 pandemic have slowed progress, Angola is now poised for sustained and vibrant economic development, building upon the foundations laid in recent years.
 Political
Stability and Credible Development Plans:
Political
Stability and Credible Development Plans:
Angola has maintained political stability since the end of the civil war in 2003. The government's recent approval of well-structured economic development plans, developed in collaboration with international institutions and consulting firms, underscores its commitment to fostering long-term growth and stability.
 Increasing Expectations and Demand from Civil Society:
Increasing Expectations and Demand from Civil Society:
Civil society in Angola is becoming more vocal, particularly through official and social media channels. There is growing impatience among the youth for tangible results, driving demand for bolder economic policies and more responsive governance.
 Private-Led Economic Development:
Private-Led Economic Development:
Angola's new economic policy prioritizes private-led development and welcomes both local and international investors. The privatization of inefficient state-owned enterprises and infrastructure assets is underway, creating opportunities for private sector engagement across various sectors.
 Favourable Investment Legislation:
Favourable Investment Legislation:
The Angolan government has enacted legislation conducive to investment, offering incentives, contractual guarantees, and measures to enhance the ease of doing business. Additionally, efforts to streamline bureaucratic processes and improve the business environment further enhance the attractiveness of investing in Angola.
 Macroeconomic Stability:
Macroeconomic Stability:
Angola's participation in an IMF-led macroeconomic restructuring program enhances the credibility of its macroeconomic environment. While challenges such as inflation persist, the devaluation of the national currency and efforts to reduce fiscal pressure contribute to greater stability.
 Endogenous Potential and Market Opportunities:
Endogenous Potential and Market Opportunities:
Angola possesses significant endogenous potential, particularly in agriculture, making it a prospective agricultural hub in Africa. The country's strategic location and geopolitical context further underscore its potential as a key player in regional and global markets.
 Development Potential:
Development Potential: Angola possesses immense potential to emerge as one of Africa's largest and most vibrant economies. With a relatively recent history of independence and a period of prolonged civil war, the country has undergone significant economic and social modernization since 2004. Although setbacks like the drop in oil prices and the COVID-19 pandemic have slowed progress, Angola is now poised for sustained and vibrant economic development, building upon the foundations laid in recent years.
 Political
Stability and Credible Development Plans:
Political
Stability and Credible Development Plans:Angola has maintained political stability since the end of the civil war in 2003. The government's recent approval of well-structured economic development plans, developed in collaboration with international institutions and consulting firms, underscores its commitment to fostering long-term growth and stability.
 Increasing Expectations and Demand from Civil Society:
Increasing Expectations and Demand from Civil Society: Civil society in Angola is becoming more vocal, particularly through official and social media channels. There is growing impatience among the youth for tangible results, driving demand for bolder economic policies and more responsive governance.
 Private-Led Economic Development:
Private-Led Economic Development:Angola's new economic policy prioritizes private-led development and welcomes both local and international investors. The privatization of inefficient state-owned enterprises and infrastructure assets is underway, creating opportunities for private sector engagement across various sectors.
 Favourable Investment Legislation:
Favourable Investment Legislation:The Angolan government has enacted legislation conducive to investment, offering incentives, contractual guarantees, and measures to enhance the ease of doing business. Additionally, efforts to streamline bureaucratic processes and improve the business environment further enhance the attractiveness of investing in Angola.
 Macroeconomic Stability:
Macroeconomic Stability:Angola's participation in an IMF-led macroeconomic restructuring program enhances the credibility of its macroeconomic environment. While challenges such as inflation persist, the devaluation of the national currency and efforts to reduce fiscal pressure contribute to greater stability.
 Endogenous Potential and Market Opportunities:
Endogenous Potential and Market Opportunities:Angola possesses significant endogenous potential, particularly in agriculture, making it a prospective agricultural hub in Africa. The country's strategic location and geopolitical context further underscore its potential as a key player in regional and global markets.
Investment policy and investment support
 Active Promotion of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
Active Promotion of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): Angola actively seeks FDI to diversify capital inflows, boost economic growth, and diversify the economy. The government's privatization program (PROPRIV) aims to sell off state-owned assets and attract private investment. Despite challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic, the government successfully privatized numerous companies and raised significant funds.
 Political
Continuation of Privatization Program:
Political
Continuation of Privatization Program:The PROPRIV program will continue through 2026, offering stakes in major state-owned enterprises such as the national airline, telecom operator, and state oil company. This initiative demonstrates the government's commitment to attracting private sector involvement and enhancing transparency in the economy.
 Modernization of Tendering Processes:
Modernization of Tendering Processes: Angola has modernized its tendering processes for public procurement to increase transparency and foster a true market economy. The government has increased the use of open tenders and implemented electronic platforms to streamline public procurement procedures.

 Trade and Investment Promotion Agency (AIPEX):
Trade and Investment Promotion Agency (AIPEX): Angola's trade and investment promotion agency, AIPEX, provides an online investment platform for investors to register their proposals. AIPEX collaborates with other institutions to promote investment opportunities through roadshows and provides support and monitoring for investment projects.
 Chambers
of Commerce and Industry:
Chambers
of Commerce and Industry:Angola has 28 chambers of commerce and industry, including those with international links, which advocate for businesses from their respective countries and facilitate business roundtables. These chambers play a crucial role in promoting investment and facilitating business interactions.
 Legislation and Investment Environment:
Legislation and Investment Environment:Angola's Private Investment Law (PIL) establishes principles for private investment, applicable to both domestic and foreign investors. The law aims to create a conducive environment for investment, with provisions for the acquisition of shares by foreign investors and regulations for fund transfers abroad.
 Investment Policy Reviews:
Investment Policy Reviews:Angola has undergone investment policy reviews by international organizations such as the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) and the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative (EITI). These reviews provide insights into the country's business and economic environments and offer recommendations for policy improvements.